Structured Cabling Design & Installation: The Ultimate Guide

In today’s interconnected world, where reliable and efficient communication is essential for businesses and organizations it plays a vital role, A well-designed and properly installed system provides the backbone for data, voice, and multimedia transmission, enabling seamless connectivity and effective communication throughout an organization. This ultimate guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this, covering key concepts, best practices, and considerations.
Contents
What is a Structured Cabling System?
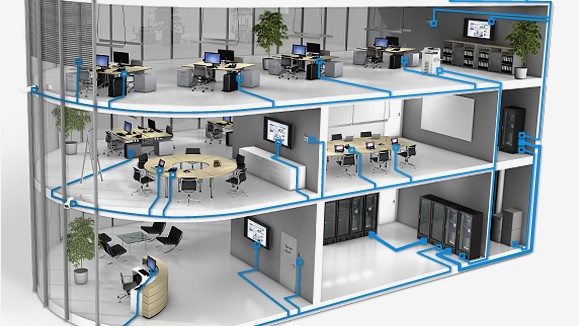
This refers to a standardized system of cabling infrastructure used in buildings or campuses to provide a comprehensive and organized approach to network connectivity. It involves the initiation of a well-planned and interconnected network of cables, connectors, and related hardware to support various communication services, such as data, voice, video, and other multimedia transmissions.
The primary goal is to establish a reliable and flexible network infrastructure that can accommodate the current and future communication needs of an organization. By implementing this system, organizations can simplify the management of their network, reduce downtime, and easily scale their infrastructure as their requirements evolve.
Here are some key components and features:
- Cables: This is typically utilizes twisted pair copper cables (e.g., Category 5e, Category 6, or Category 6a) for data transmission and fiber optic cables for high-speed and long-distance connections.
- Patch Panels: These are hardware units that provide a centralized termination point for all the cables, allowing easy and organized connectivity between different devices and network equipment.
- Patch Cords: These short cables with connectors at both ends are used to establish temporary or permanent connections between devices and patch panels.
- Racks and Cabinets: These are used to mount and organize network equipment, such as switches, routers, and servers, in a secure and easily accessible manner.
- Keystone Jacks: These are modular connectors that snap into wall plates or patch panels to provide a connection point for devices like computers, phones, or other network equipment.
What to Look for in the Design of Structured Cable?
When designing this system, there are several important factors to consider. Here are some key elements to look for in this:
Scalability & Performance and Bandwidth:
Ensure that the Cable infrastructure can accommodate future growth and expansion. Consider the potential increase in network devices, bandwidth requirements, and the ability to easily add or modify cabling as needed. The cabling system should support high-performance networks, such as Gigabit Ethernet or higher. It should provide adequate bandwidth to meet the current and future data transmission needs of the organization.
Standards Compliance & Cable Management:
Follow industry standards, such as those provided by the Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Compliance with standards ensures interoperability, compatibility, and ease of maintenance. Effective cable management is crucial for organizing and maintaining the cable system. Look for solutions that include appropriate cable trays, racks, labels, and pathways to minimize cable congestion, improve airflow, and ease troubleshooting.
Reliability Redundancy and Future-proofing:
Aim for a design that minimizes downtime and provides redundancy where necessary. Use redundant cable paths, consider backup power solutions, and incorporate failover mechanisms to ensure network availability. Anticipate emerging technologies and trends when designing the cable system. Consider the potential adoption of technologies like Power over Ethernet (PoE), wireless access points, or Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Build in flexibility to accommodate these advancements.
Documentation and Cable Length:
Maintain accurate and up-to-date documentation of the cable infrastructure. This includes cable labeling, network diagrams, test results, and equipment locations. Proper documentation simplifies troubleshooting, maintenance, and future upgrades. Plan cable lengths carefully to avoid excessive cable runs and signal degradation. Proper routing and segregation of data, voice, and power cables can help minimize interference and maintain signal integrity.
Quality Components and Compliance with Building Codes:
Use high-quality cable and connectivity components from reputable manufacturers. This ensures better performance, reliability, and compatibility with industry standards. Ensure compliance with local building codes and regulations when designing the cable system. This includes considerations for fire safety, environmental factors, grounding, and electrical codes.
Guide To Structured Cabling Installation
The installation process involves several steps:
- Site Survey: Conduct a thorough site survey to assess the existing infrastructure, identify potential challenges, and determine the optimal placement of equipment and cable pathways.
- Preparing Pathways: Prepare the pathways for cable initiation, including conduits, cable trays, and wall/ceiling penetrations. Ensure compliance with building codes and regulations.
- Cable Initiation: Install the cables according to the designed layout. Properly terminate and label each cable to ensure easy identification and maintenance.
- Testing and Certification: Perform comprehensive testing of each cable to verify its performance and compliance with industry standards. Use cable testers to check for continuity, attenuation, and signal quality.
- Documentation: Maintain accurate documentation of this, including cable layouts, labeling schemes, test results, and any modifications made during initiation. This documentation serves as a valuable reference for future maintenance and upgrades.
- Post-Initiation Cleanup: Clean up the work area, remove any debris or unused materials, and ensure a neat and professional initiation.
How Does a Standardized System of Cables Work?
This refers to the standardized system of cables, connectors, and related hardware used to establish a reliable and organized telecommunications infrastructure within a building or campus. It provides the foundation for various communication technologies, such as voice, data, and video transmission. Here’s a general overview of how its works:
Planning and Design:
Before implementing this, a thorough planning and design phase is necessary. This involves assessing the communication requirements, determining the layout of the building, and identifying the appropriate cable standards and components.
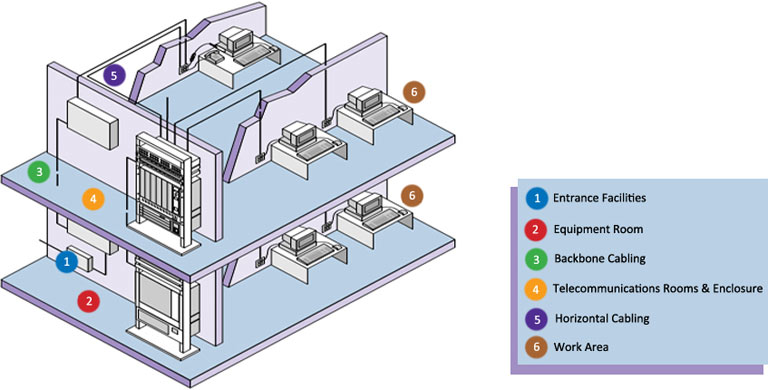
Horizontal cable :
Starts with the initiation of horizontal cable, which connects the main distribution area (such as a server room) to individual workstations or devices. This typically involves running twisted-pair copper cables or fiber optic cables from a patch panel in the main distribution area to wall-mounted outlets near each work area.
Backbone Cabling:
Backbone cabling establishes the interconnections between various telecommunication rooms or equipment rooms within a building. It consists of high-capacity cables, such as fiber optic cables or large copper cables, which carry data between different floors or sections of the building. The backbone cabling connects the different network devices, such as switches or routers, enabling data to flow across the entire network infrastructure.
Patch Panels and Patch Cords:
Patch panels serve as the central termination points for the horizontal and backbone cable. They provide a structured interface for connecting cables to network equipment. Patch cords, which are short, pre-terminated cables, connect the patch panels to the network devices, such as switches or servers. These patch cords can be easily plugged and unplugged, allowing for flexibility in network configuration.
Cable Management:
Proper cable management is essential to maintain an organized and efficient system. Cable trays, racks, and conduits are used to route and support the cables, keeping them organized, protected, and easily accessible. Labeling and color-coding the cables also help with identification and troubleshooting.
The foundation of a reliable and efficient communication infrastructure, By following best practices and considering key factors during the design and initiation process, organizations can benefit from increased flexibility, reduced downtime, simplified management, and long-term cost savings. Regular maintenance and adherence to industry standards contribute to the longevity and performance of this system. When it comes to structured cabling installation, hiring a professional company can make a significant difference. These companies bring expertise, experience, and industry knowledge to ensure a successful initiation and optimal performance of the system. They can handle the complexities of designing the cable infrastructure, selecting the right components, and implementing best practices.